India, the country with numerous Southeastern monsoon and vast agricultural lands varying in climate, has recently begun suffering from various extreme weather events. Be it harmful cyclones or lengthy droughts, a more significant percentage of the Indian subcontinent is affected by nearly all of the described meteorological temperatures. The most commonplace relates to factors from the Indian Ocean, acting as the main catalyst for the weather in that region.
The Indian Ocean and its role in extreme weather events
One of the rivers nearby is the Indian Ocean, which is the third-largest body of water in the world and greatly influences the climate of the neighboring countries, including India. Its warm waters provide the moisture and energy required for the formation of cyclones, while seasonal fluctuations contribute to both late and erratic monsoon season. Therefore, the country must tackle heavy rainfall and prolonged drought, making devastating floods and droughts a common wdbos occurrence.
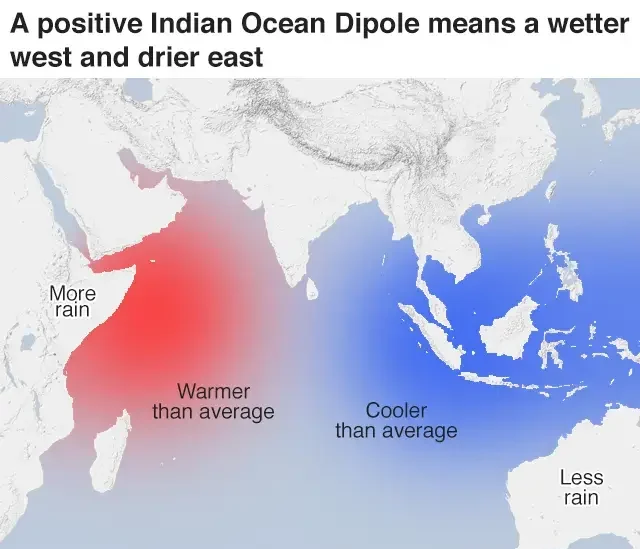
The Indian Ocean Dipole is a frequent occurrence fueling this fire , affecting the weather patterns throughout the region. A positive phase occurs when the western part of the Indian Ocean warms up relative to the east. This setup leads to additional rainfall over the Indian subcontinent. Conversely, negative psychologists significantly reduce rainfall and can result in drought conditions.

Historical extreme weather events in India
India has a long history of extreme weather events causing considerable damage. For instance, in May 2020, the Eastern coast was devastated by Cyclone Amphan, which featured unimaginable 185 km/h winds. The cyclone was deadly, killing over a hundred people and destroying infrastructure along with agriculture. The eastern coasts have witnessed such cyclones multiple times over the past several decades, but the severity of Cyclone Amphan has made it one of the deadliest on record.
Furthermore, one of the most significant weather events were the Indian Drought of 1876-1878, which was caused by the lack of monsoon in India. The event was catastrophic, leading to failing crops, famine, and thousands losing their lives. Such events in India’s crisis history rapid repetitive enough such events might take place again, so India has to prepare as much as possible.
Causes and factors contributing to extreme weather events in the Indian Ocean region
Extreme weather occurrences in the Indian Ocean region are brought about by a combination of natural and anthropogenic factors. The natural factors include local variations in sea surface temperature, atmospheric pressure systems, and wind patterns. The El Niño-Southern Oscillation system – an atmospheric phenomenon where the tropical Pacific Ocean warms and cools – brings about these natural anomalies in the Indian Ocean region.
However, in the last decade, human-induced climate change has been a massive driver of the extreme events. Global warming raises temperatures over the Indian Ocean and creates an elevated platform for the cyclic intensification of cyclones. Further, modified wind patterns as per climate change ripple effects disturb the Indian monsoon and bring irregular rainfall and above-average dry spells.
Effects of extreme weather events on India’s economy, agriculture, and infrastructure
In addition to negatively affecting public health and natural resources, extreme weather events are also costly for India’s economy, agriculture, and infrastructure. For example, intense rainfalls lead to massive flooding, which further results in the destruction of houses, infrastructure, and agricultural lands. Flood often leads to considerable economic damages. The floods in Kerala in 2019 are regarded as one of the worst flooding events in the history of the state.
Millions were left without homes, which further led to the destruction of a considerable part of the infrastructure. Although heavy rainfalls are often associated with extreme weather events, including oceanic cyclones, another extreme phenomenon involves droughts. Since agriculture in India is highly depended on monsoons, drought results in crop failures. As a result, millions of farmers lose their means of subsistence. The government of India also supports farmers in situations of crop loss with the help of different programs, including the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana .
Climate change and its influence on extreme weather events in the Indian Ocean
Climate change is causing extreme weather events to become more frequent and intense in the Indian Ocean region. The rising ocean temperatures of the ocean provide the energy necessary for cyclone formation and intensification. Besides the more energetic precipitation, warmer ocean waters lead to increased evaporation which means higher moisture content in the atmosphere, resulting in higher rainfall intensities during cyclones.
Furthermore, disrupted wind systems under global climate change make the monsoon season very unstable with irregular patterns of heavy rain and prolonged periods of drought. This is a massive danger for India’s agriculture, water supply capacity, and overall socio-economic stability. More intense variability in monsoon precipitation may cause large water shortages throughout much of the country. It may affect not only food production but also prevent millions of people from gaining access to drinking water.
Efforts and initiatives to mitigate the impact of extreme weather events in India
Recognizing the urgent need to address the impacts of extreme weather events, India has undertaken various efforts and initiatives to enhance resilience and mitigate the effects of climate change. The National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), launched in 2008, outlines strategies and measures to address climate change adaptation and mitigation.
One such initiative is the establishment of early warning systems for cyclones and floods. The India Meteorological Department (IMD) has been working to improve forecasting capabilities, allowing for timely evacuation and preparedness measures. Additionally, the government has invested in infrastructure development, such as flood control measures and water management systems, to minimize the impact of extreme weather events.
Adaptation and resilience strategies for dealing with extreme weather events in India
Building resilience and adapting to the changing climate are essential for India’s sustainable development. The adoption of climate-smart agricultural practices, such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and the use of drought-tolerant crop varieties, can help farmers cope with the challenges posed by extreme weather events. Integrated water resource management, including the conservation and efficient use of water, is crucial for ensuring water availability during droughts.
Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, such as cyclone shelters, flood-resistant buildings, and resilient transportation systems, is key to minimizing the impact of extreme weather events on human lives and livelihoods. Moreover, promoting community-based disaster risk reduction and preparedness is vital for building resilience at the grassroots level.
The role of government and stakeholders in addressing extreme weather events
Addressing the challenges posed by extreme weather events requires a collective effort from the government, stakeholders, and the general public. The government plays a crucial role in formulating and implementing policies and regulations to mitigate the impact of climate change and enhance resilience.
Stakeholders, including non-governmental organizations, research institutions, and the private sector, have a vital role to play in developing innovative solutions and technologies to address the challenges posed by extreme weather events. Public awareness and education campaigns can help raise awareness about the impacts of climate change and the importance of adaptation and resilience.

The need for collective action to tackle extreme weather events in India
India’s vulnerability to extreme weather events due to the Indian Ocean and climate change necessitates urgent action. The frequency and intensity of cyclones, floods, and droughts are expected to increase in the coming years, posing significant challenges to the country’s socio-economic development.
Collective action, involving the government, stakeholders, and the general public, is crucial for tackling these challenges. Investing in climate-resilient infrastructure, promoting sustainable agriculture practices, and strengthening early warning systems are key steps towards building resilience and adapting to the changing climate. If you found this article insightful, we invite you to explore our coverage on similar climate-related issues impacting regions worldwide, such as our article on Iran and Israel. Together, let’s stay informed and engaged in shaping a more resilient and sustainable future for all.

